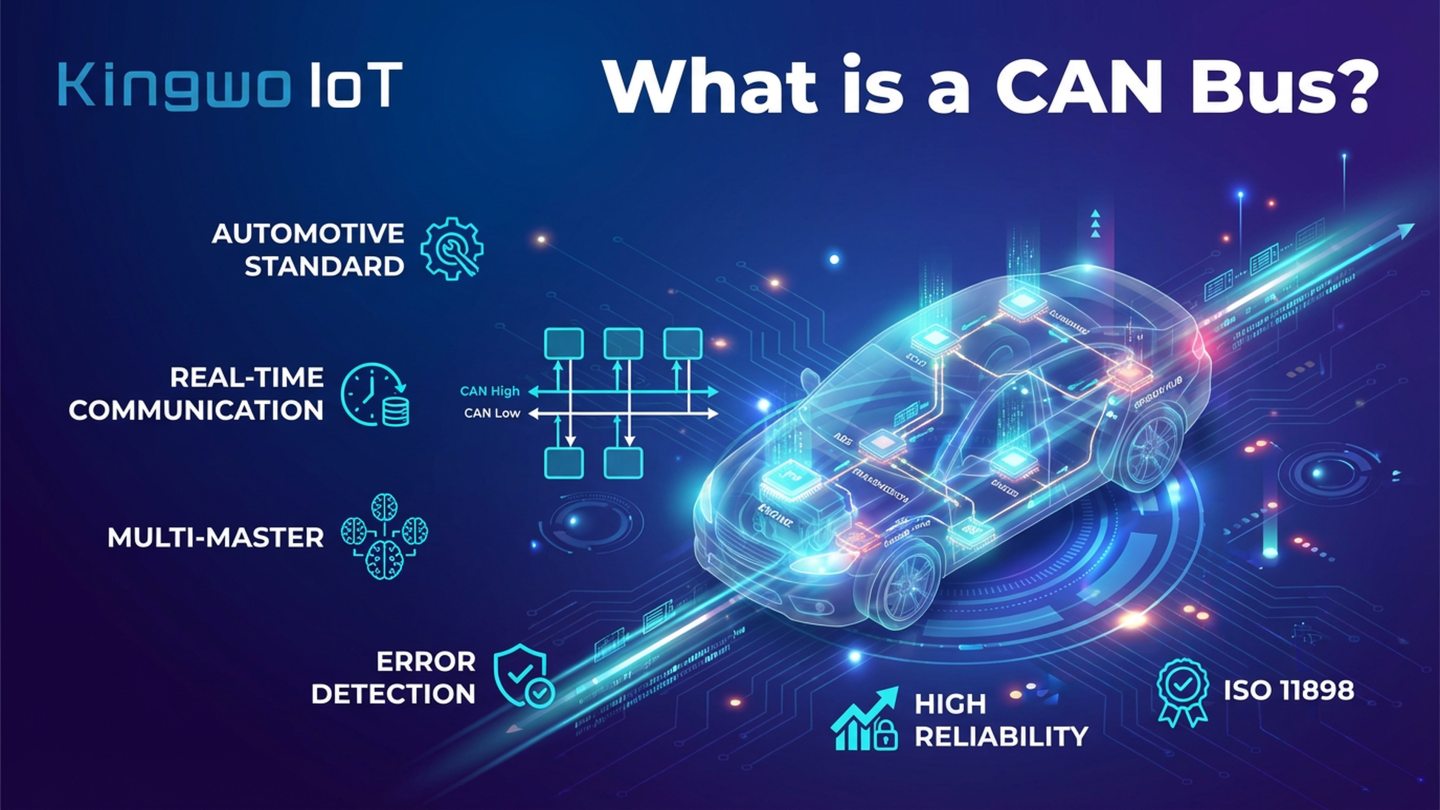
The #ControllerAreaNetwork (CAN) bus is a robust, message-based communication system designed to enable electronic control units (ECUs) within vehicles and industrial equipment to communicate efficiently without relying on a central host computer. Originally developed for automotive applications, CAN bus has become a foundational technology for modern fleet telematics, industrial automation, and embedded systems.
In fleet operations, CAN bus data allows operators to gain direct visibility into vehicle performance, operational status, and mechanical health. Parameters such as fuel consumption, engine load, braking behavior, and fault codes can be accessed in real time, supporting informed decisions around maintenance, efficiency, and asset utilization.
When applied correctly, CAN bus data enables predictive maintenance, improves fuel efficiency, and helps fleet operators reduce downtime and operating costs.
CAN bus is a standardized communication protocol that allows multiple ECUs to exchange data over a shared two-wire network. Instead of using complex point-to-point wiring, CAN enables all nodes on the network to broadcast messages that can be received and interpreted by other nodes based on message identifiers.
A helpful way to understand CAN bus is to think of it as a digital highway. Every ECU can transmit messages onto the bus, and each message includes a priority-based identifier that determines how it is handled. This approach ensures that critical messages—such as those related to engine control or braking—are transmitted with higher priority than less time-sensitive data.
Modern vehicles typically use multiple CAN variants depending on system requirements. High-speed CAN supports data rates up to 1 Mbps for time-critical functions such as powertrain and safety systems. Low-speed, fault-tolerant CAN operates at lower speeds for body electronics and comfort features. CAN FD (Flexible Data Rate) further extends capabilities by allowing larger data payloads and higher data rates when needed.
CAN bus was conceived in the early 1980s to address the growing complexity of vehicle electronics. As vehicles incorporated more electronic systems, traditional wiring approaches became heavier, less reliable, and harder to maintain.
The CAN protocol was formally introduced in the mid-1980s and saw its first production deployment in the early 1990s. By the mid-to-late 1990s, it had become the standard in-vehicle networking technology across the global automotive industry.
Today, CAN bus extends far beyond passenger vehicles. It is widely used in commercial fleets, construction equipment, agricultural machinery, medical devices, and maritime systems—anywhere reliable, real-time communication between embedded systems is required.
CAN bus uses a broadcast communication model over a shared, twisted-pair cable consisting of CAN High and CAN Low lines. All ECUs connected to the bus listen continuously and decide whether incoming messages are relevant based on their identifiers.
When the bus is idle, both lines remain at approximately 2.5 volts, indicating a recessive state. During data transmission, the transceiver drives CAN High and CAN Low in opposite directions, creating a voltage differential that represents a dominant state. This differential signaling makes CAN bus highly resistant to electrical noise, which is critical in automotive and industrial environments.
CAN FD enhances this model by allowing dynamic switching between arbitration speed and data speed, enabling larger payloads—up to 64 bytes—while maintaining backward compatibility with classic CAN systems.
A CAN bus network consists of three main components: ECUs, transceivers, and the physical bus itself. Each ECU includes a CAN controller responsible for protocol handling and message arbitration, along with a transceiver that converts digital signals into differential voltages on the bus.
This decentralized architecture improves reliability. There is no single point of failure, and if one ECU stops functioning, the rest of the network can continue operating normally. Built-in error detection mechanisms—such as cyclic redundancy checks, bit monitoring, and acknowledgment validation—ensure data integrity across the network.
CAN bus has become essential in commercial and industrial systems due to its efficiency, reliability, and scalability.
One major advantage is reduced wiring complexity. By allowing multiple systems to share a single communication bus, CAN significantly lowers wiring weight and installation complexity, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and easier maintenance.
Real-time communication is another key benefit. Priority-based message arbitration ensures that critical data is transmitted with minimal latency, even in high-traffic networks.
CAN bus is also designed for fault tolerance. Advanced error detection mechanisms allow ECUs to identify and isolate faults before corrupted data affects system operation.
Standardized diagnostics further enhance its value. Through #OBD interfaces and diagnostic tools, technicians can access fault codes and system data consistently across different vehicle platforms, simplifying fleet maintenance and troubleshooting.
Finally, CAN bus offers long-term cost efficiency by reducing hardware complexity, improving system reliability, and enabling data-driven maintenance strategies.
In fleet environments, CAN bus serves as a primary data source for telematics systems. Raw vehicle data collected from the CAN network can be transformed into actionable insights related to fuel efficiency, driver behavior, maintenance planning, and asset utilization.
By combining CAN data with positioning and connectivity technologies, fleets gain a comprehensive view of vehicle performance and operational trends. This supports more accurate maintenance scheduling, reduced fuel consumption, and better-informed replacement and sustainability decisions.
Kingwo IoT works with CAN bus data as part of a broader connected vehicle and asset intelligence ecosystem. Our solutions are designed to reliably collect, transmit, and interpret CAN bus information alongside positioning and sensor data, enabling organizations to turn low-level signals into meaningful operational insights.
By focusing on stable hardware integration, efficient data transmission, and scalable platforms, Kingwo IoT helps fleet operators, solution providers, and system integrators build telematics solutions that are reliable, adaptable, and aligned with real-world operational needs.
Rather than treating CAN bus data as an isolated input, Kingwo IoT approaches it as a foundational layer within a connected system—supporting smarter maintenance strategies, improved efficiency, and long-term operational visibility across diverse industries.

English

French

Portuguese

Spanish
