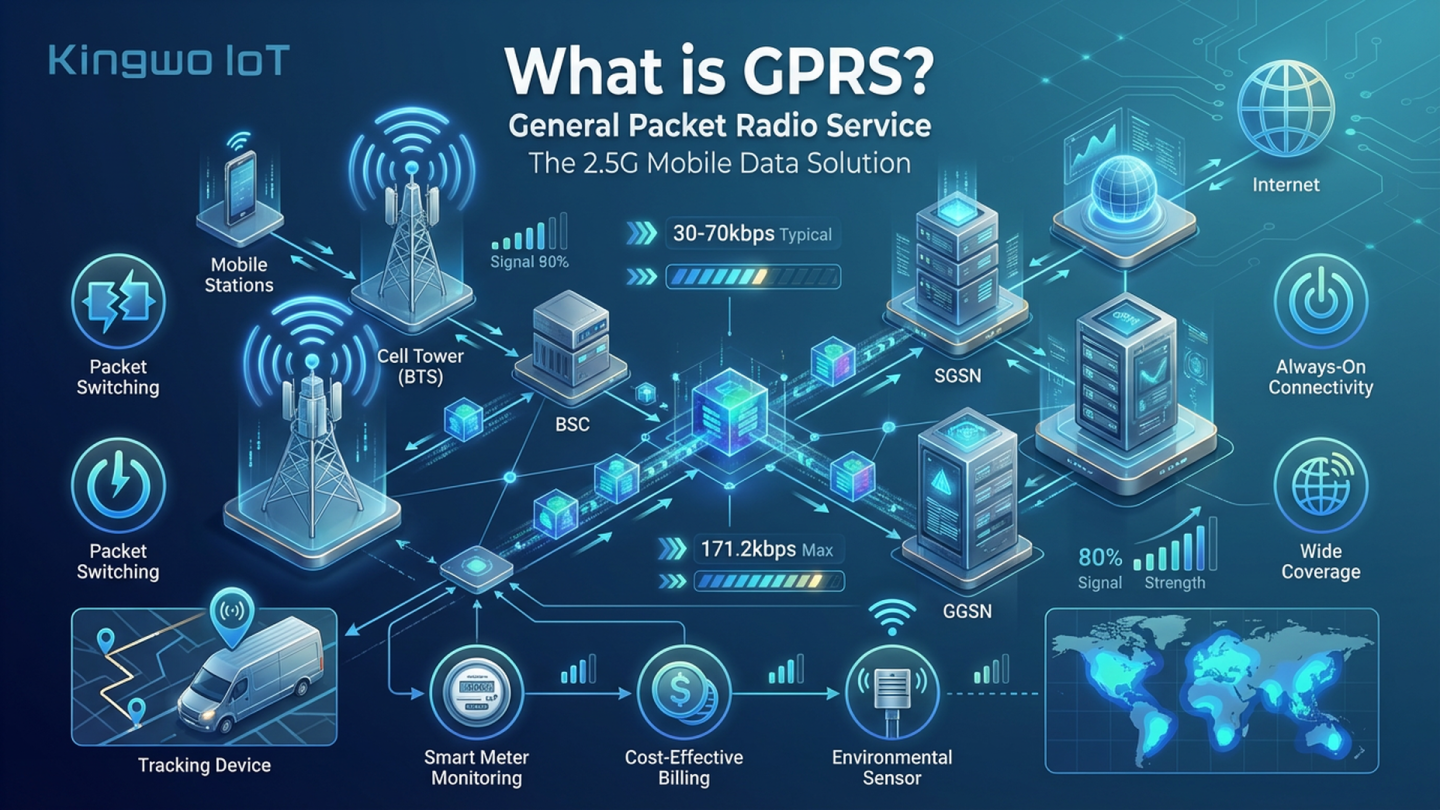
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a foundational wireless data technology that enables packet-based communication across 2G and 3G cellular networks. For modern fleets, GPRS plays a vital role in supporting real-time tracking, monitoring and communication between drivers, dispatchers and fleet managers. By transmitting continuous data packets securely and efficiently, GPRS enhances operational intelligence and helps organizations maintain reliable visibility over vehicle and asset performance.
GPRS delivers timely information about traffic conditions, route changes, weather, and customer locations. With this data, fleets can optimize route planning, reduce travel time, conserve fuel and strengthen overall fleet management efficiency.
GPRS overlays a packet-switched communication layer on top of the existing GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) network. While traditional GSM voice calls rely on dedicated channels, #GPRS transmits segmented data packets across any available channels, making data transmission more efficient and scalable.
Fleet managers and drivers use this packet-based communication to exchange vehicle diagnostics, performance insights and operational updates. Below are the core technical elements that define how GPRS supports fleet operations.
Each data packet includes its own routing and destination information, allowing multiple independent data streams to travel simultaneously over a single radio channel. This structure is ideal for fleets that need ongoing communication without bandwidth congestion. Packet switching minimizes costs and improves the reliability of fleet-wide data exchange.
By dividing data into small packets, GPRS provides peak data rates reaching up to approximately 115 kbps in practical application. Fleets can allocate network time slots according to transmission needs, ensuring smooth delivery of critical data such as vehicle status, driver alerts or dispatch updates.
Unlike dial-up systems that disconnect after each session, GPRS maintains a persistent IP connection. This allows drivers and dispatchers to communicate continuously without re-establishing the connection each time. For fleet operations, this means faster decision-making and uninterrupted visibility of moving assets.
Two key components make GPRS secure and mobile-friendly:
Together, these support nodes ensure safe, seamless and uninterrupted communication for fleets operating across broad geographic regions.
GSM originally launched in the early 1990s and quickly expanded across global regions. As fleets grew and required more advanced data transfer capabilities, GSM was no longer sufficient for real-time operations.
GPRS was introduced in 2000 and widely adopted in 2001, enabling mobile internet, email and data-driven communication to flourish. It also provided backward compatibility with GSM networks, making it easy for enterprises and fleets to upgrade existing systems. GPRS later served as the foundation for more advanced 3G, 4G and 5G networks.
1. Higher Data Speeds
GPRS significantly increases the data transfer speed compared to earlier GSM systems. With peak rates reaching near 171 kbps in certain configurations, fleets can manage sensor data, tracking information and diagnostics much more efficiently.
2. Efficient Network Resource Usage
GPRS’ continuous connectivity and packet-switched structure reduce bandwidth waste and support faster communication across the fleet. Secure and encrypted transmission ensures high reliability for sensitive operational data.
3. Flexible and Cost-Effective Billing
Fleet operators can choose pricing models based on data usage or connection time, allowing organizations to control operating costs effectively while maintaining reliable network performance.
Real-Time Vehicle Tracking
Telematics devices use GPRS to transmit GPS coordinates, route progress and geofencing alerts directly to the fleet platform. This enables real-time decision-making and ensures that drivers receive the most efficient routes on time.
Risk Monitoring and Driver Safety
GPRS supports the transmission of safety-related insights such as seatbelt usage, harsh braking, speeding incidents, reverse driving or weather alerts. These data points help reduce accident risk and improve driver accountability.
Predictive Maintenance
GPRS-enabled telematics devices send data on fuel consumption, engine diagnostics, idle times and digital key usage. This helps fleet managers detect early warning signs and schedule maintenance before costly failures occur.
Sustainability and Environmental Data
For sustainability-focused fleets, GPRS can send data about fuel consumption, CO₂ emissions and driver behavior. For EV fleets, GPRS supports battery monitoring, performance tracking and EVSA (Electric Vehicle Sustainability Assessment).
Compliance and Regulatory Reporting
GPRS facilitates the transmission of electronic driver logs, vehicle inspections, fuel tax reports and temperature monitoring. These insights help fleets maintain regulatory compliance and avoid penalties.
Expandability and Integration
As fleets adopt new technologies, GPRS supports upgrades such as API integrations, advanced analytics platforms, hardware enhancements and dispatch software to improve operational efficiency.
Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Communication
GPRS enables M2M communication even without traditional internet connectivity, ensuring continuous tracking in remote regions. For fleets traveling across rural or low-signal routes, this capability is critical.
Network Congestion and Performance
Data speeds may decline when many users share the same network resources. Latency or network congestion can delay communication, limiting real-time optimization capabilities.
Security Risks
Although GPRS includes fundamental security protocols, it can still face vulnerabilities such as spoofing and data tampering. Fleets may require additional encryption to protect sensitive information.
Technology Obsolescence
As 4G and 5G networks dominate modern communication, GPRS—originally designed for 2G networks—faces increasing maintenance costs and reduced relevance. However, many fleets still rely on GPRS for its wide coverage and consistent availability.
Kingwo IoT is a global provider of intelligent telematics and IoT solutions dedicated to helping fleets achieve safer, smarter and more efficient operations. With a strong focus on innovation, Kingwo delivers advanced GPS tracking systems, telematics hardware and cloud-based fleet management platforms designed for real-time decision-making.
Our mission is to empower businesses with reliable, scalable and future-ready connectivity technologies—from GPRS to 4G, LTE-M, NB-IoT and beyond. Kingwo’s vision is to build an interconnected world where fleets of all sizes can operate with full transparency, complete control and maximum efficiency. We are committed to advancing telematics technology to help our partners reduce costs, enhance safety and move confidently into the future of intelligent mobility.

English

French

Portuguese

Spanish
